Type Of Industrial Chain Sprockets
- Share
- Issue Time
- Apr 16,2024
Summary
Industrial chain sprockets encompass various types, including Type A, B, C, and D categorized by hubs, and plain bore, finished bore, and taper bore based on hole types. They also vary by the number of rows, materials like carbon steel and stainless steel, and specialized designs like idler, QD bushing, split, double pitch, and DS sprockets. Customization for specific applications is available, ensuring versatility and adaptability in industrial settings.

Type of Industrial Chain Sprockets?
Industrial Chain sprockets come in a variety of types, which can be classified according to different hubs: A-hub, B-hub, C-hub, and D-hub sprockets; according to the type of bore, they can be divided into plain bore sprockets, finished bore sprockets, and taper bore sprockets. They can also be classified based on the number of rows, such as single-row sprockets and multi-row sprockets. Based on materials, they can be divided into carbon steel sprockets and stainless steel sprockets (the two most common materials, but other materials can also be customized according to your specific needs). Additionally, there are idler sprockets, QD bushing sprockets, split sprockets, double pitch sprockets, and double sprockets for two single chains (abbreviated as DS sprockets). Specialty sprockets can also be customized according to different applications.
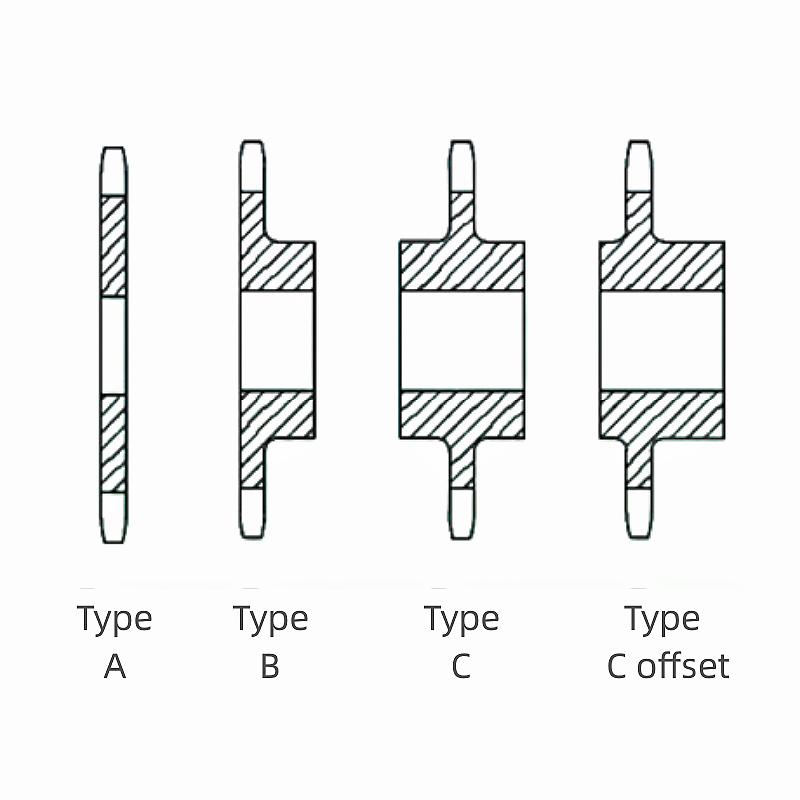
Sprocket Hub Types
Different types of sprockets feature distinct hubs. A hub refers to the added thickness around the central plate of a sprocket, excluding the teeth.
Type A sprockets consist solely of a plate with no added thickness or hubs.
Type B sprockets feature a hub on one side.
Type C sprockets have hubs of equal thickness on both sides of the plate.
Type C offset or Type D sprockets also have two hubs, but each hub has a different thickness, resulting in an asymmetrical sprocket.
These variations cater to different applications; Type A and B sprockets snugly fit against equipment, while Type C sprockets, being larger, require more thickness to support weight.
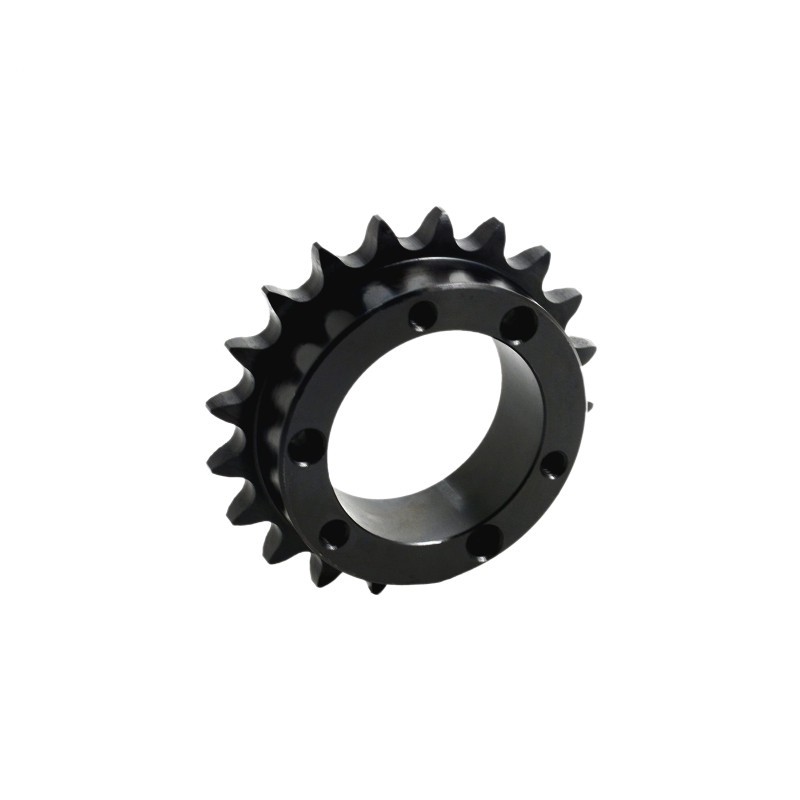
Sprocket Bore Types
The sprocket bore refers to the inside diameter of the sprocket and its method of attachment to the shaft.
"Plain bore/Pilot bore" is associated with A-hub, B-hub, and C-hub sprockets, where no special machining is performed for keyways or set screws. These sprockets only feature a hole to accommodate the shaft diameter, often requiring additional machining before installation.
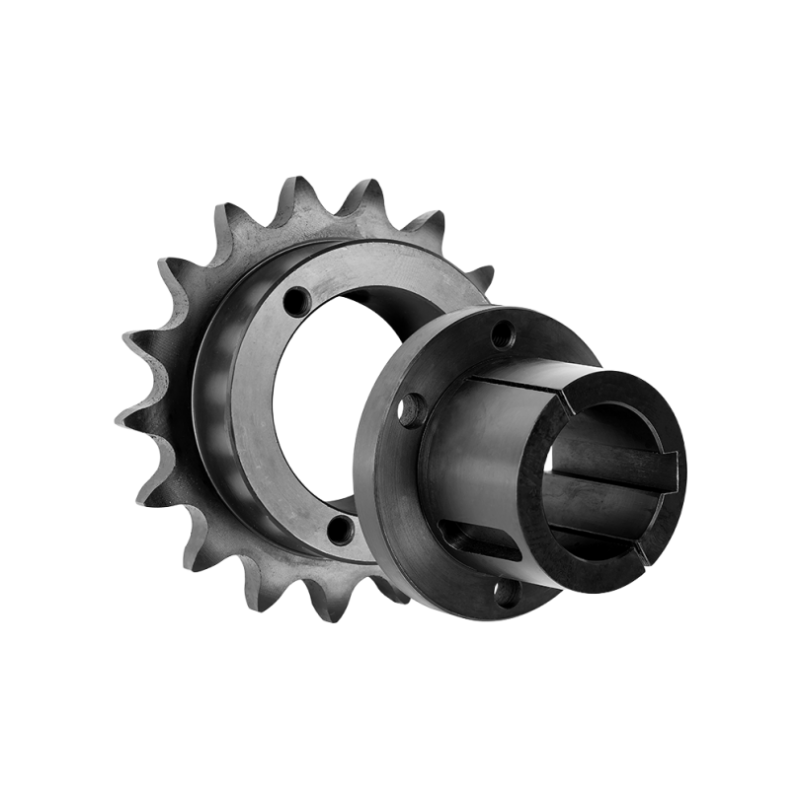
"Finished bore" is linked with B- and C-style sprockets, where the hub's inside diameter is machined to fit a specific shaft diameter. This configuration includes a standard keyway and set screws, with CTS® providing two set screws for added clamping force. Finished bore hubs can also be machined to meet non-standard yet specific requirements based on the application needs. (Refer to Fig. 6 for a standard finished bore sprocket.)
"Taper bore" refers to a specialized type of sprocket bore design that features a tapered inner diameter. This design allows for a tight and secure fit onto a shaft with a matching taper, ensuring optimal transmission of power and torque. Taper bore sprockets are commonly used in applications where precise alignment and maximum torque transmission are critical, such as in heavy machinery, conveyor systems, and automotive components. The taper bore design facilitates easy installation and removal while providing a reliable and durable connection between the sprocket and shaft.
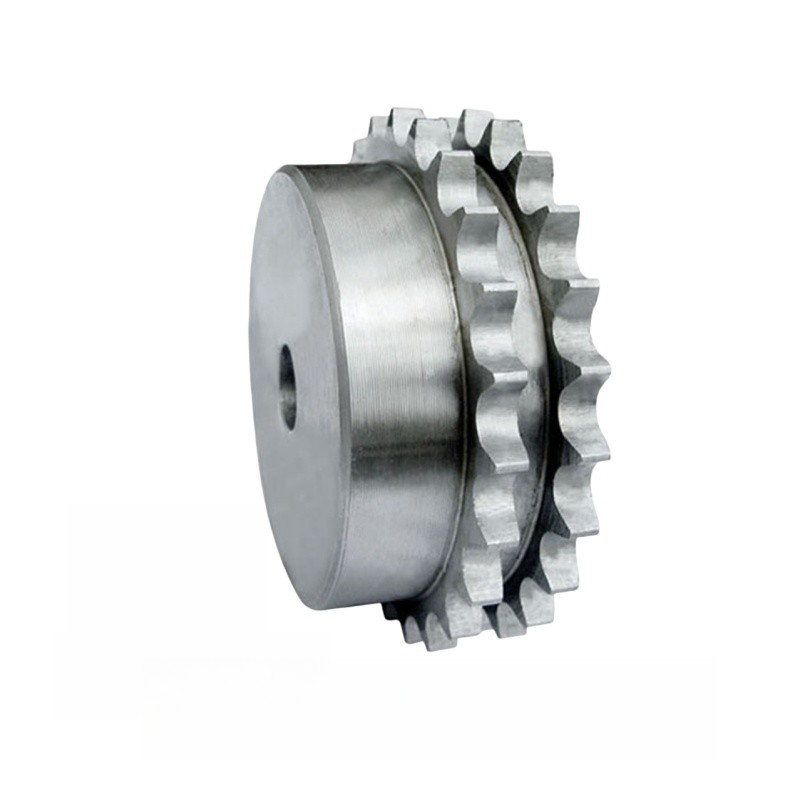
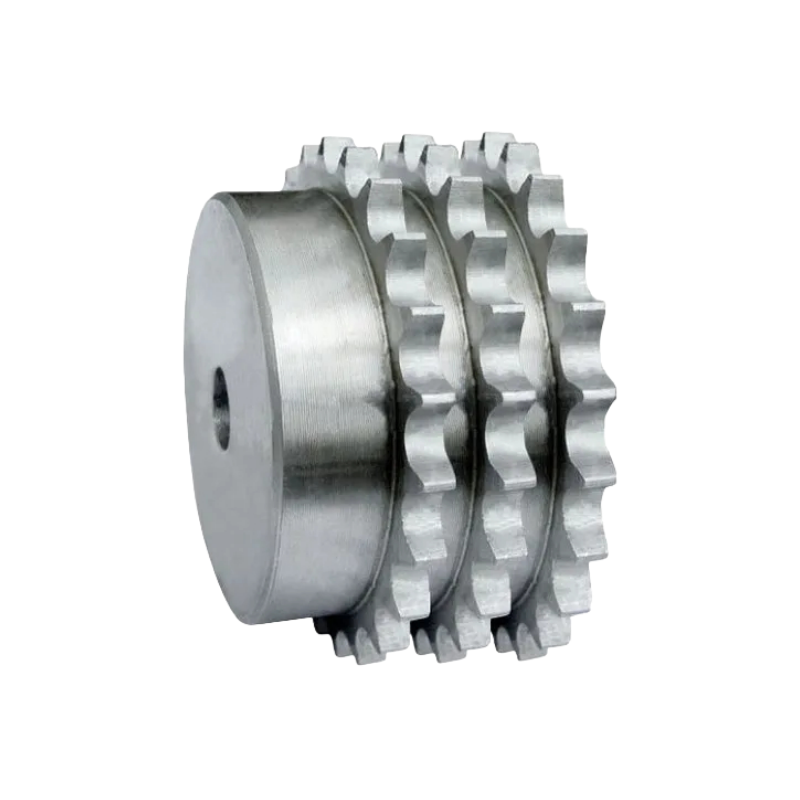
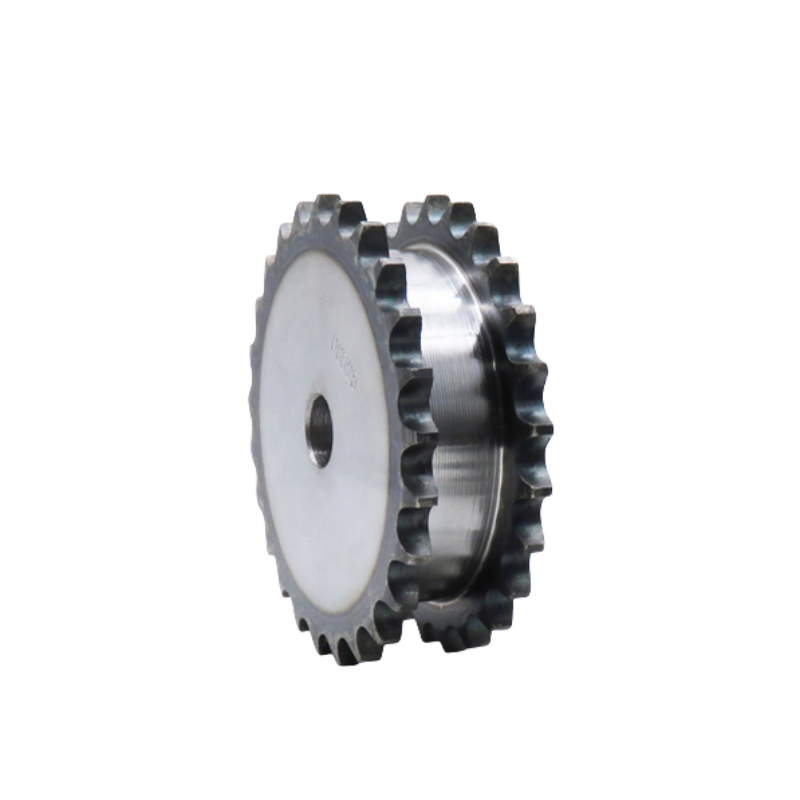
The Num of Rows of Sprocket
The number of rows of a sprocket refers to the arrangement of teeth on the sprocket's surface. Sprockets can be classified based on the number of rows of teeth they possess, such as single-row sprockets, double-row sprockets, or multi-row sprockets. This classification is essential for determining compatibility with corresponding chains and transmission systems.
Materials of Chain Sprockets
Sprockets can be made from various materials, each offering distinct properties and suitability for different applications. Common materials include:
Carbon Steel: Known for its strength and durability, carbon steel sprockets are widely used in industrial applications due to their cost-effectiveness and high load-bearing capacity.
Stainless Steel: Stainless steel sprockets offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications in harsh environments or industries requiring high cleanliness standards, such as food processing or pharmaceuticals.
Specialty Materials: In addition to carbon steel sprockets and stainless steel sprockets, industrial chain sprockets can also be made from specialty materials tailored to specific requirements, such as heat-treated steels for high-temperature applications or exotic alloys for extreme conditions.
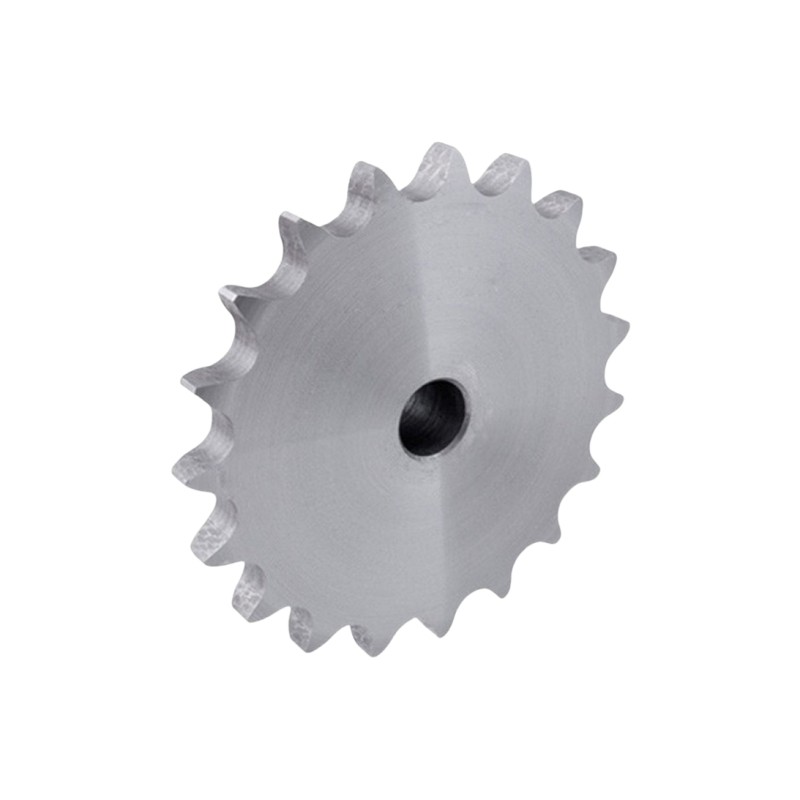

Carbon Steel Industrial Sprockets
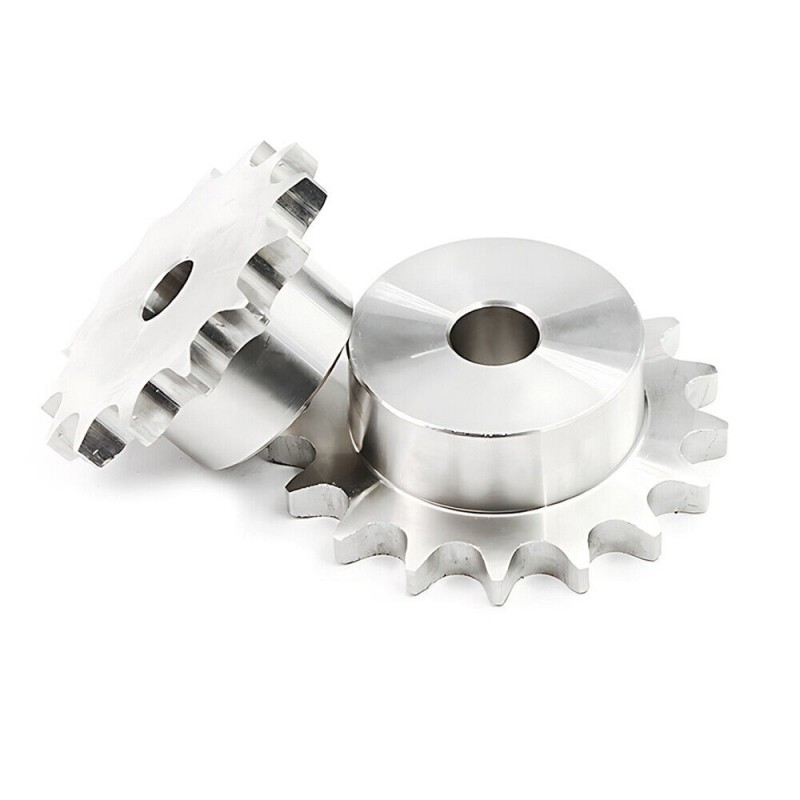

Stainless Steel Industrial Sprockets
Surface treatment of Chain Sprockets
Surface treatment of industrial chain sprockets is crucial for enhancing their performance, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion. Common surface treatments include:
Heat Treatment: Heat treatment processes such as carburizing, quenching, and tempering improve the hardness, strength, and wear resistance of sprocket surfaces, extending their lifespan in demanding applications.
Black Oxide: Black oxide treatment is a surface treatment method applied to chain sprockets to enhance appearance, provide corrosion resistance, and improve wear resistance through the formation of a protective black oxide layer.
Plating: Plating with materials like chrome, zinc, or nickel enhances corrosion resistance and provides a protective layer against environmental factors, extending the sprocket's service life.
Coating: Coating processes such as powder coating or painting provide a protective layer on the sprocket surface, improving resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and chemical exposure.
Shot Peening: Shot peening induces compressive stress on the surface of the sprocket, improving fatigue resistance and reducing the risk of stress corrosion cracking.
Anodizing: Anodizing aluminum sprockets creates a protective oxide layer on the surface, improving corrosion resistance and providing a decorative finish.
Passivation: Passivation of stainless steel sprockets removes impurities and contaminants from the surface, improving corrosion resistance and enhancing the material's natural protective properties.
Each surface treatment method offers unique benefits and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application and the desired performance characteristics of the sprocket.
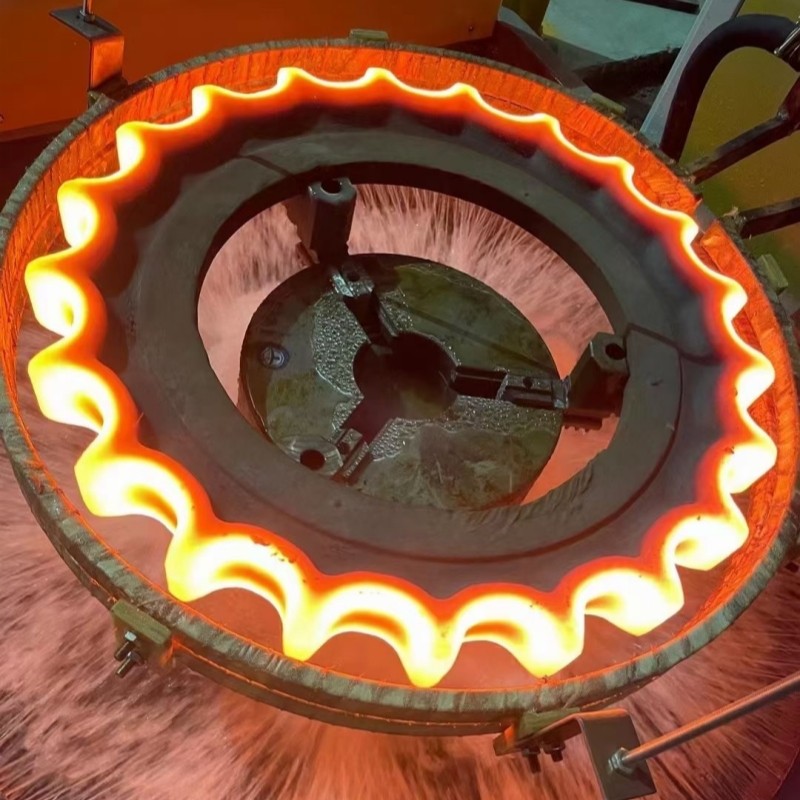

Heat Treatment Of Industrial Sprockets
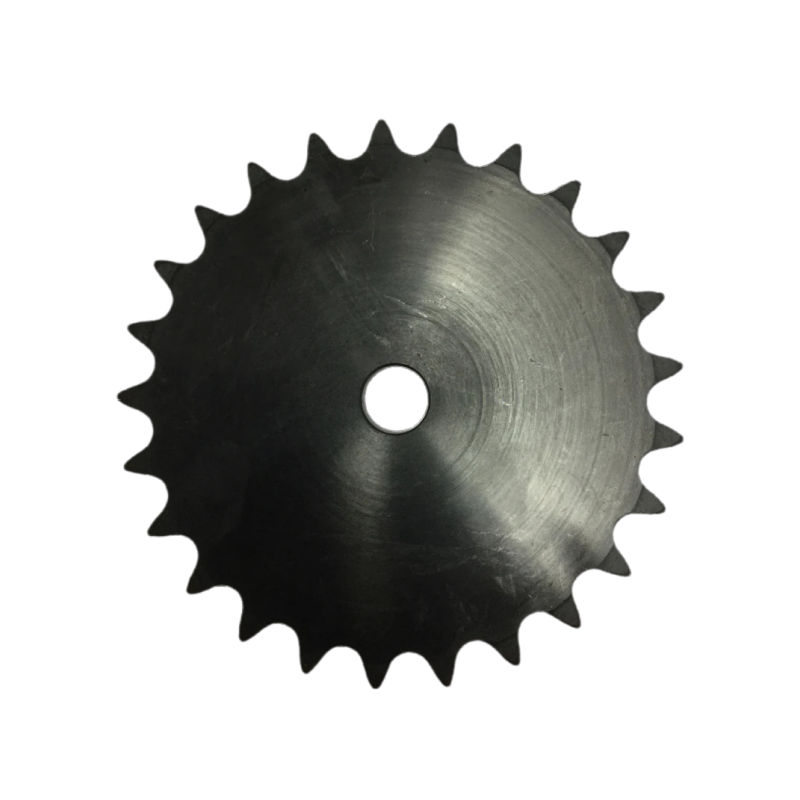

Industrial Sprockets with Black Oxide Treatment
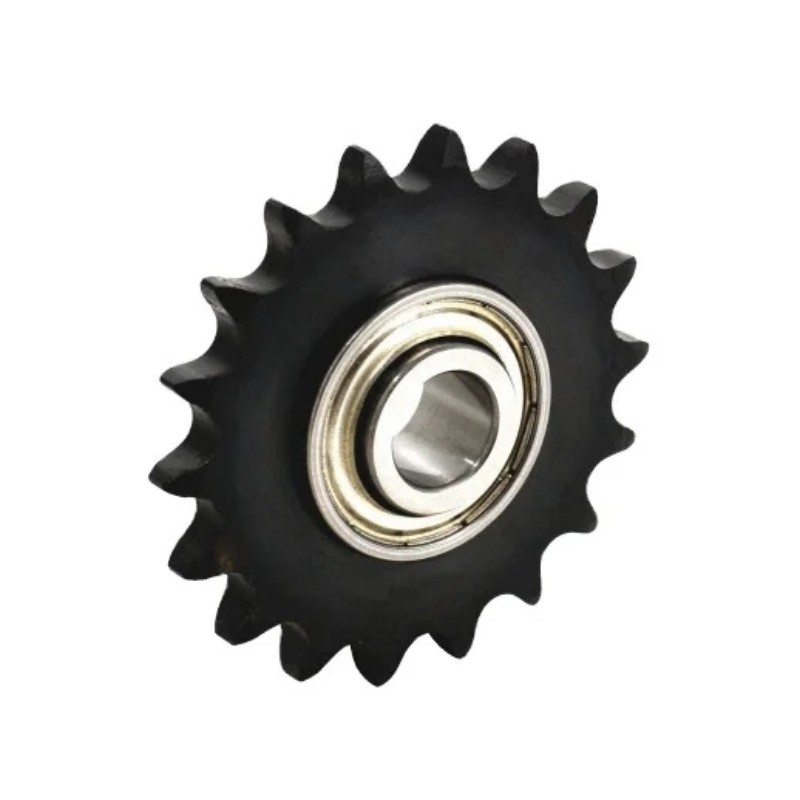
Other Types of Sprockets
CTS® is a professional Industrial chain sprocket manufacturer, we can also supply specialty sprockets that are tailored to specific applications, offering customized features to meet unique requirements.
For over fourteen years, CTS® has dedicated itself to crafting top-quality chain sprockets and drive components. Our specialization extends to providing superior power transmission parts and custom-designed products. If you're seeking a reliable Roller Chain sprocket solution, look no further. With a full range of industrial sprockets at your disposal, our experienced team is ready to assist you in finding the perfect fit for your needs. Trust CTS® to deliver excellence and efficiency every step of the way.
If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us, CTS® professional technicians will be happy to help you!