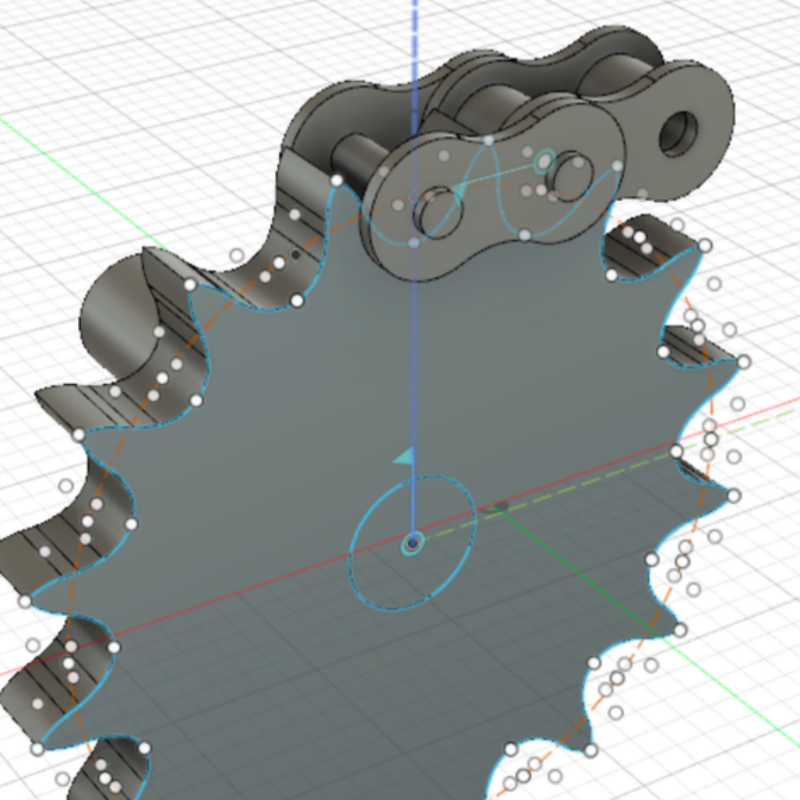
Innovation Design and Manufacturing Solution For Conveyor Chain Sprockets
- Share
- Issue Time
- Sep 19,2025
Summary
Learn how conveyor chain sprockets are engineered with innovative design solutions, encompassing tooth profiles, material selection, heat treatment, and surface finishing, to ensure durability, precision, and efficiency in conveyor systems.

Odd VS. Even Sprocket Tooth Configurations
Tooth configuration is a critical factor in sprocket performance. Designers often choose between odd-numbered teeth and even-numbered teeth, depending on application needs.
Odd Number Teeth (e.g.,13,17,19):
✔ Advantage: Reduces repetitive wear on the same chain link, distributing load evenly.
✔ Advantage: Extends chain life by alternating the engaging links.
✘ Limitation: May cause slight vibration in some systems.
Even Number Teeth(e.g.,12,16,20):
✔ Advantage: Provides smoother rotation in high-speed applications.
✔ Advantage: Easier to manufacture in standardized sizes.
✘ Limitation: Increases repetitive stress on certain chain links.
Application Tip:
Use odd-number sprockets for heavy-duty, low-speed conveyors to maximize chain life.
Use even-number sprockets for high-speed conveyors where vibration control is critical.
Material Selection for Conveyor Chain Sprocket
The material used directly impacts sprockets' durability and performance. Different industries require different solutions:
| Material | Advantages | Applications |
| Carbon Steel | Strong, suitable for most conveyors | General industry |
| Cast Iron | High wear-resistance, good damping properties | Heavy-duty conveyors |
| Stainless Steel | Corrosion-resistant, hygienic | Food & beverage, pharma |
Alloy Steel | Superior strength, suitable for heat treatment | Mining, cement, heavy loads |
Choosing the right material helps balance cost, performance, and lifespan. For example, food-grade conveyors almost always require stainless steel sprockets.
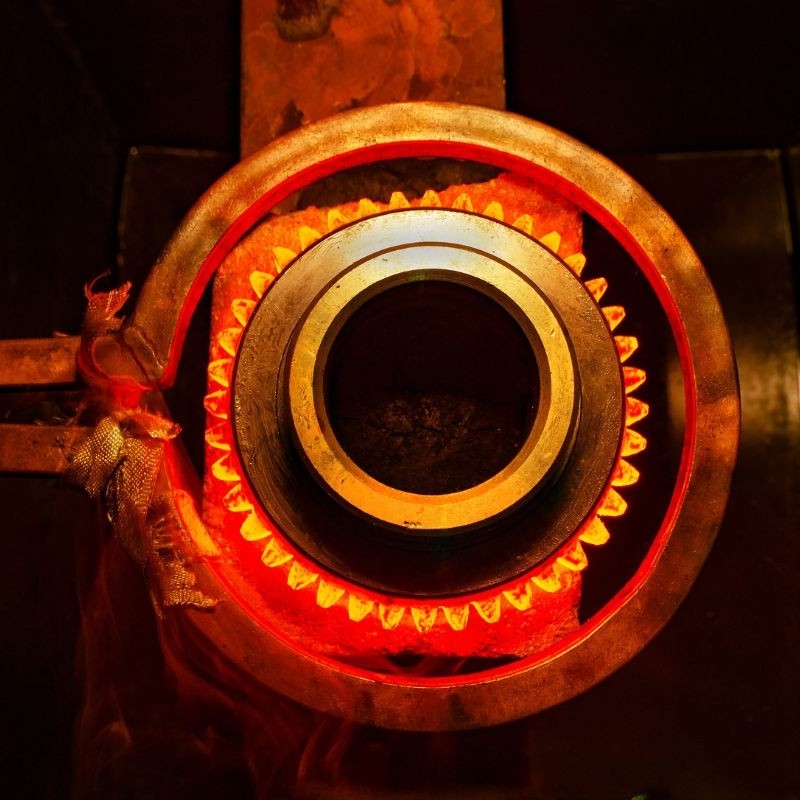
Heat Treatment and Surface Hardening Techniques
Conveyor chain sprockets endure constant contact and load from chains, so heat treatment is essential.
Common sprocket heat-treatment techniques
Case Hardening
Hardens the tooth surface while maintaining a tough core
Through Hardening
Ensures consistent hardness throughout the sprocket
Induction Hardening
Targets only the tooth area for improved wear resistance
Sprocket surface treatments
Black Oxide
Adds corrosion resistance, reduces glare
Zinc Plating
Protects against rust in moderate environments
Nitriding
Creates a hard,wear-resistant outer layer

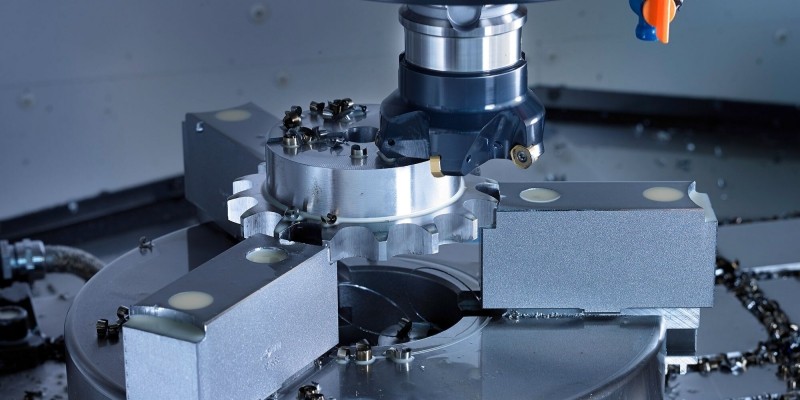
Precision Manufacturing Processes
Modern sprocket manufacturing combines traditional methods with CNC precision.
Key steps include:
· CNC Machining: Ensures accurate pitch diameter and tooth geometry.
· Keyway Cutting &Bore Finishing: Guarantees proper shaft fit and alignment.
· Quality Control: Hardness testing, dimensional checks, fatigue testing.
Choosing the Right Conveyor Chain Sprockets

Selecting the correct sprocket requires consideration of:
1. Chain Compatibility-Match sprocket pitch and tooth count with chain specifications.
2. Operating Environment-Corrosive,high-temperature, or hygienic environments demand specific materials and coatings.
3. Maintenance Requirements-Choose designs that allow easy replacement or reduced lubrication needs.
CTS® | Professional Sprockets Factory
As a professional industrial sprocket manufacturer, CTS-ChinaTransmissionS offers a comprehensive range of high-quality sprockets.

If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
CTS® professional technicians will be happy to help you!
FAQs
What makes conveyor chain sprockets different from roller chain sprockets?
Conveyor sprockets are typically larger, designed for heavier loads, and customized for slow-moving conveyor applications, while roller chain sprockets are used in high-speed power transmission.
How does heat treatment improve Conveyor Chain sprocket life?
Heat treatment hardens the tooth surface, making it more resistant to wear while maintaining core toughness to handle heavy loads.